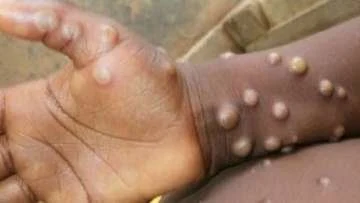
Mpox Cases in India: In response to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) declaration of the ongoing Mpox outbreak as a Public Health Emergency of International Concern (PHEIC), Union Health Secretary Apurva Chandra issued an advisory to all States and Union Territories on Sunday, urging them to enhance preparedness and surveillance for the disease.
The advisory follows WHO’s decision on August 14, 2024, to declare Mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) a global health emergency. This is the second such declaration for Mpox under the International Health Regulations, 2005, considering the rising trend of cases, particularly in the Democratic Republic of Congo, and the spread to newer East African nations, including Burundi, Kenya, Rwanda, and Uganda. The emergence of a new mutant variant, Clade IIb, has raised further concerns.
Clinical Trends and Spread
According to WHO, most Mpox cases have affected young males with a median age of 34 years, and sexual contact remains the most commonly reported mode of transmission. Common symptoms include rashes (systemic or genital) and fever, with nearly 52% of cases involving individuals living with HIV.
Though India has not reported any new Mpox cases during the current outbreak, the Health Ministry continues to closely monitor the situation. India’s Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme and airport health units have been instructed to stay vigilant, with enhanced screening for international travelers. Additionally, the laboratory network under the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has been strengthened to test suspect cases.
Key Public Health Actions
The Union Health Secretary highlighted several key public health measures to prevent Mpox transmission in India, including:
- Guidelines Dissemination: The Ministry’s guidelines for managing Mpox are to be widely circulated, providing protocols for handling and treating cases.
- Updated Surveillance: The National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) has issued an updated CD-Alert detailing case definitions, contact tracing strategies, and infection control practices.
- Public Health Preparedness: States and districts are advised to review preparedness at the health facility level, ensure isolation facilities, and train healthcare personnel.
- Strengthened Community Awareness: State AIDS Control societies are to be on high alert, improving public awareness to ensure timely reporting of suspected cases.
The advisory underscores the importance of coordinated efforts at national and state levels to prevent any possible outbreaks in the country. The Union Health Ministry has reassured that it will continue to monitor the evolving situation and take necessary steps to protect public health.
Keep watching our YouTube Channel ‘DNP INDIA’. Also, please subscribe and follow us on FACEBOOK, INSTAGRAM, and TWITTER