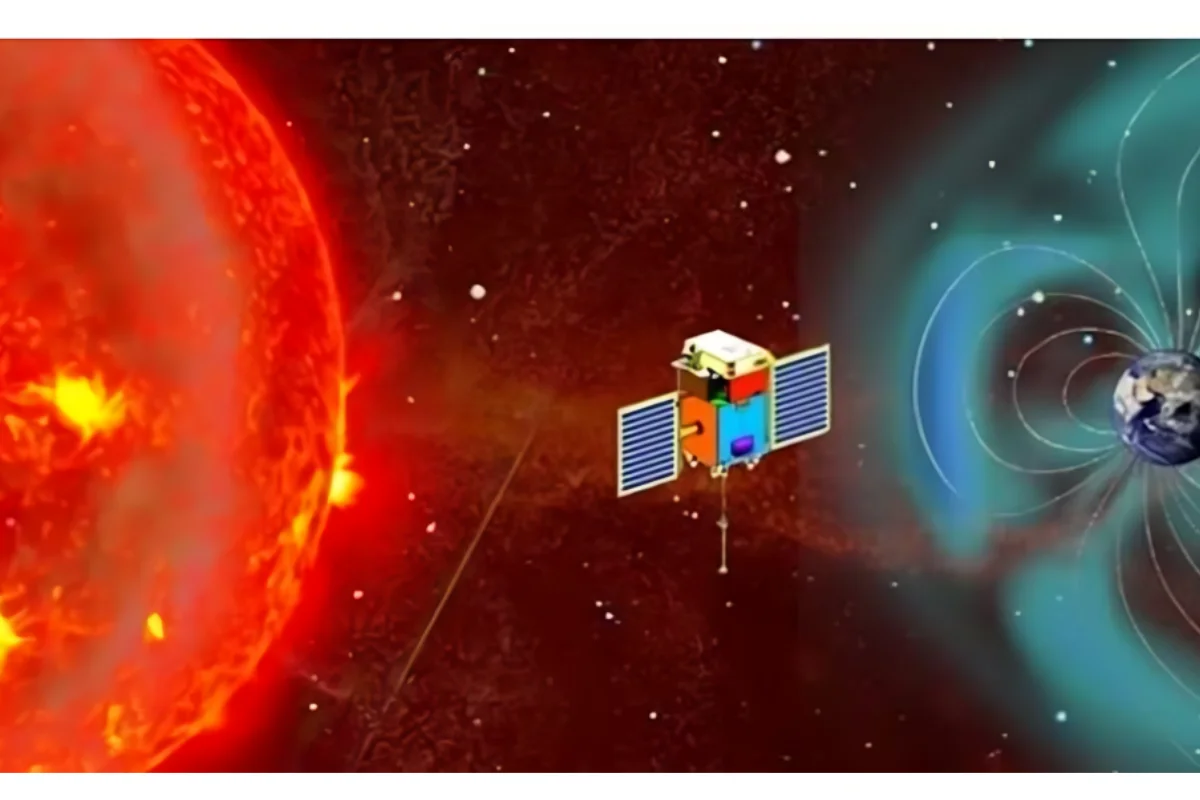
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) achieves a significant milestone as the Aditya L1 spacecraft successfully reaches its destination, the halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system. This marks ISRO’s ambitious debut mission to study the Sun, and the spacecraft is poised to observe the Sun’s corona and understand its extreme heat.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi Commends ISRO’s Achievement
Prime Minister Narendra Modi applauds the achievement, highlighting the dedication of Indian scientists in realizing this complex space mission. The successful insertion of Aditya L1 into its designated orbit signifies a remarkable feat for India in the field of space exploration.
Aditya L1’s Mission and Importance
Aditya L1’s primary objective is to observe the Sun’s corona, offering insights into the star’s dynamic behavior and potential solar phenomena that can impact Earth’s space environment. The spacecraft, positioned at the L1 point, 1.5 million km from Earth, is equipped with seven payloads designed to study various layers of the Sun.
Payloads and Collaborations in Aditya L1 Mission
Aditya L1’s seven payloads are developed by different Indian laboratories, showcasing collaborative efforts. These include instruments such as VELC, SUIT, ASPEX, PAPA, SoLEXS, HEL1OS, and Magnetometer, each contributing to the comprehensive study of the Sun’s photosphere, chromosphere, and corona.
Significance of Aditya L1’s Mission
The successful insertion into the halo orbit positions Aditya L1 to begin its observational phase, contributing valuable data for better understanding the Sun’s impact on Earth. The mission holds promise for advancements in solar science and space exploration.
Keep watching our YouTube Channel ‘DNP INDIA’. Also, please subscribe and follow us on FACEBOOK, INSTAGRAM, and TWITTER