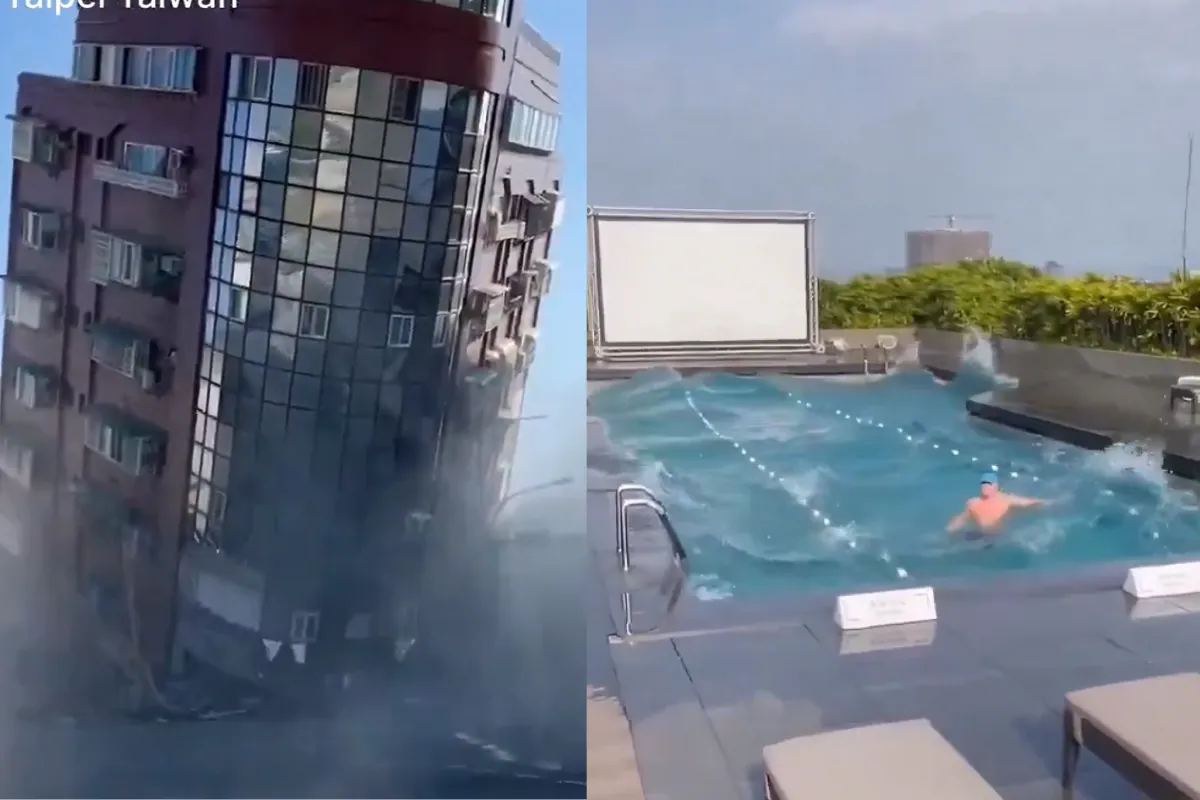
Nepal Earthquake: A nation known for its stunning natural beauty, has also gained notoriety for its vulnerability to earthquakes. The Himalayan nation gets over the terrible earthquake that struck on November 3 and claimed 153 lives, Nepal was struck by another earthquake on Monday night, measuring 5.6 on the Richter scale.
In the previous four days, Nepal has experienced three earthquakes. Certain regions of north India, particularly the Delhi-NCR area, also experienced tremors. Around 8,000 houses, both public and private, were damaged by the Friday earthquake that struck western Nepal’s districts of Jajarkot and Rukum West, according to officials.
In recent years, the region has experienced several devastating seismic events, leaving people wondering what causes these quakes and how science explains them.
Nepal’s Geologic Setting:
Nepal is located in a seismically active region, nestled within the Himalayan mountain range. This makes it particularly susceptible to earthquakes. The Himalayas, formed by the collision of the Indian and Eurasian tectonic plates, are still actively converging. The ongoing interaction between these massive plates generates immense geological stress, which is released in the form of earthquakes.
Tectonic Plate Movements:
The primary cause of earthquakes in Nepal is the tectonic plate movement. The Indian plate, to the south of Nepal, is slowly but steadily moving northward, pushing against the Eurasian plate. As these plates interact, they become locked together due to friction. The pressure continues to build up until it is released in a sudden and violent manner, resulting in an earthquake.
Focus and Epicenter:
Earthquakes originate underground, at a point known as the “focus” or “hypocenter.” The depth of this focus can vary, and it greatly influences the impact of the earthquake. Shallower foci tend to cause more surface damage, while deeper foci may result in less destruction. In the case of Nepal, many earthquakes have their epicenters near or within the country, contributing to the high level of seismic activity.
Seismic Waves:
When an earthquake occurs, it generates seismic waves that radiate outward from the epicenter. There are two main types of seismic waves: primary (P-waves) and secondary (S-waves). P-waves are faster and less destructive, while S-waves are slower and can cause significant damage. In addition, surface waves can develop as the seismic energy reaches the Earth’s surface, causing further destruction.
Steps to earthquake safety
- Secure heavy furniture: Anchor bookshelves, cabinets, and large appliances to prevent them from falling during an earthquake.
- Create an emergency kit: Prepare a kit with essential supplies like water, non-perishable food, first aid, flashlights, and batteries.
- Plan escape routes: Identify safe exit paths in your home or workplace, and practice evacuation drills with your family or colleagues.
- Stay indoors: If you’re indoors during an earthquake, take cover under a sturdy piece of furniture, away from windows, and protect your head.
- Drop, cover, and hold on: If you can’t take cover, drop to the ground, cover your head, and hold onto something sturdy to minimize injury.
- Stay informed: Listen to local authorities for updates and follow their instructions.
- Know your surroundings: Be aware of potential hazards like gas lines, and learn how to turn them off.
- Check your building’s safety: Ensure your home or workplace complies with earthquake-resistant construction standards.
- Prepare an emergency contact list: Share this with family and friends so you can stay connected during a crisis.
- Educate yourself: Learn about earthquake preparedness and recovery to be better equipped for a seismic event.
Also Read: ABC sends Chandrababu Naidu to 14-day judicial remand in corruption case
Keep watching our YouTube Channel ‘DNP INDIA’. Also, please subscribe and follow us on FACEBOOK